Pizza Hut Target Market Analysis
Understanding a company’s target market is crucial for crafting effective marketing strategies, optimizing product development, and sustaining long-term growth. A well-defined target audience allows businesses to connect authentically with consumers and remain relevant in a fast-changing marketplace. This is especially true in the highly competitive food service industry, where brand loyalty, convenience, and taste preferences dictate success.
Pizza Hut, a global leader in the pizza restaurant sector, has become a household name since its founding in 1958. Known for its iconic pan pizzas, dine-in service model, and extensive delivery network, Pizza Hut operates in more than 100 countries. Despite shifting consumer behaviors and fierce competition from brands like Domino’s and Papa John’s, Pizza Hut continues to adapt its offerings to appeal to evolving consumer needs.
This article explores the Pizza Hut target market in depth. We’ll analyze who Pizza Hut’s primary customers are, how the brand segments and markets to these groups, and what strategies it uses to stay ahead. We’ll also compare Pizza Hut’s audience with key competitors and discuss the brand’s advantages and challenges in capturing consumer attention. Whether you’re in the food industry or studying brand strategy, this deep dive into Pizza Hut’s audience offers actionable insights on modern market targeting.
Contents
Who is Pizza Hut’s Target Audience?
The Pizza Hut target market is broad, but the brand strategically tailors its messaging and product offerings to core customer segments with shared lifestyle habits and dining preferences. The primary audience includes families, young adults, and working professionals who value convenience, affordability, and familiar flavors.
Pizza Hut appeals strongly to families with children, typically within the middle-income bracket, ranging from $40,000 to $100,000 annual household income. These customers often seek an easy, budget-friendly dining solution that satisfies both kids and adults. Pizza Hut’s menu, which includes combo meals, shareable sides, and kid-friendly flavors, is designed with these households in mind. Its dine-in experience, still popular in some markets, also caters to family outings.
Another vital segment is young adults aged 18–34, including college students and early-career professionals. This group is highly digital, cost-conscious, and inclined toward takeout or delivery. Pizza Hut addresses these habits through app-based ordering, online promotions, and bundling deals. With fast service and frequent deals, it positions itself as both a casual indulgence and a go-to meal during busy weeks.
Moreover, Pizza Hut resonates with customers who seek brand familiarity. Many were introduced to the brand in childhood, making nostalgia a key emotional driver. In global markets like India or the Middle East, the brand adapts its menu for local tastes while preserving its core American pizza identity.
This multi-tiered approach allows Pizza Hut to maintain broad appeal while staying focused on consumers who seek comfort food, value, and convenience. The Pizza Hut target market isn’t just about demographics—it’s about capturing moments when easy, enjoyable meals are a priority.
Pizza Hut Target Market Segmentation and Marketing
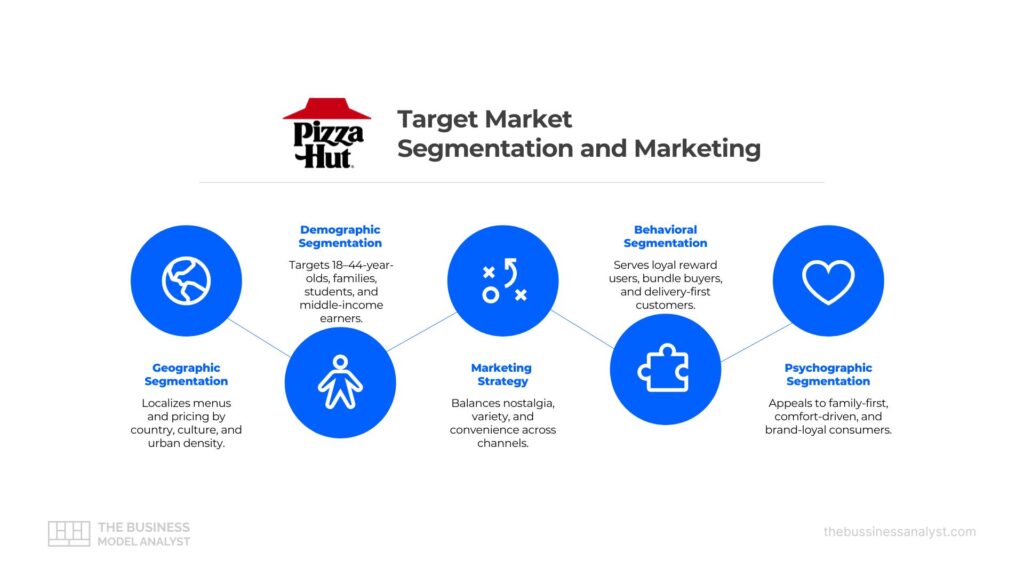
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer market into smaller, more manageable groups based on shared characteristics. These segments enable companies to tailor marketing efforts, optimize product development, and better meet the specific needs of their audience.
Pizza Hut applies segmentation strategically to address the diverse preferences of its global audience. While the brand has mass-market appeal, it adjusts offerings and messaging based on distinct consumer behaviors, lifestyles, and regional preferences. This allows Pizza Hut to effectively market to both budget-conscious families in the U.S. and young professionals in urban areas abroad.
Pizza Hut’s segmentation strategy spans four key types:
- Demographic Segmentation – Based on age, income, gender, and education level, helping the brand identify key consumer profiles.
- Geographic Segmentation – Adapted to regions, countries, and urban versus rural differences, this guides regional menu innovations and pricing.
- Behavioral Segmentation – Focused on user habits, frequency of purchases, and brand loyalty, informing strategies for upselling and customer retention.
- Psychographic Segmentation – Focused on values, lifestyles, and emotional preferences, shaping Pizza Hut’s brand tone and promotional messages.
Each segmentation type gives Pizza Hut the tools to engage its audience more precisely and remain competitive in a saturated market.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation involves categorizing a market based on quantifiable characteristics such as age, gender, income level, and education. This method provides clear insights into who is buying a product, how much they can spend, and what their life stage might indicate about their preferences.
For Pizza Hut, demographic segmentation reveals a diverse but strategically targeted customer base. One of its strongest segments is families with children, especially those in the 25–44 age range. These customers are typically parents looking for quick, reliable meal options that are both affordable and enjoyable for children. Pizza Hut appeals to this group by offering large portions, family meal bundles, and consistent quality that minimizes the stress of mealtime decisions.
Another major demographic includes young adults aged 18–34, a tech-savvy group that values convenience, flavor variety, and digital access. College students and early-career workers within this bracket are often budget-conscious, which makes them responsive to promotions and loyalty programs. Pizza Hut meets these needs through mobile ordering, discounted lunch combos, and late-night delivery options.
In terms of income, Pizza Hut primarily serves middle-income households, though it also appeals to both lower-income customers via value deals and higher-income patrons through premium pizza offerings and seasonal menu items. This income flexibility broadens its reach across social classes without diluting the brand.
Gender segmentation plays a lesser but still noticeable role. Marketing materials often portray shared meal experiences—such as date nights, game nights, or family dinners—where both men and women are seen enjoying Pizza Hut together, reinforcing the brand’s image as a social food choice.
Pizza Hut also considers education level indirectly by aligning product messaging with consumer awareness of quality ingredients or health-conscious choices. For example, offering thinner crusts or vegetarian options reflects subtle shifts aimed at educated consumers with more nuanced dietary preferences.
By using demographic data, Pizza Hut tailors everything from portion sizes and pricing to promotional language, ensuring its broad appeal remains grounded in targeted execution.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides the market based on location—countries, regions, climates, or population density. This approach helps brands adapt their offerings to cultural tastes, regional pricing norms, and logistical realities. For Pizza Hut, which operates in over 100 countries, geographic segmentation is central to its global success.
In the United States, Pizza Hut positions itself as a familiar, affordable dining option with an emphasis on takeout, delivery, and family meals. Marketing here often focuses on tradition, game-day gatherings, and comfort food, resonating with suburban and urban families alike. In contrast, urban centers see more investment in digital delivery platforms and app-based convenience, targeting younger, busier demographics.
In international markets, Pizza Hut localizes its menu and branding to align with regional culinary expectations. In India, for example, the chain offers vegetarian-only locations and popular menu items like Paneer Tikka Pizza, aligning with cultural dietary norms. In Japan, offerings may include seafood toppings and smaller portion sizes to match local eating habits and taste preferences.
Pricing strategies also vary by region. In countries like Indonesia or Mexico, Pizza Hut may position itself as a more premium brand due to local economic factors. Meanwhile, in Australia and the UK, Pizza Hut competes directly with Domino’s in the value-for-money category, offering competitive combo deals.
Additionally, Pizza Hut considers urban vs. rural market needs. Urban areas typically have a higher demand for app-based ordering and fast delivery, while rural areas may rely more on dine-in formats and community-oriented promotions.
This regional customization ensures that while the brand maintains its global identity, it remains locally relevant—an essential balance in today’s competitive foodservice industry.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on how consumers interact with a brand—how often they buy, what they purchase, and how loyal they are. It’s about understanding customer habits and designing experiences that meet those patterns. For Pizza Hut, this segmentation is critical in driving repeat orders, maximizing value per transaction, and enhancing customer loyalty.
A key segment for Pizza Hut includes frequent users—customers who order regularly, often on weekends or during promotions. These users tend to be time-strapped professionals, families with children, or students, and they respond strongly to loyalty incentives. Pizza Hut targets them through its Hut Rewards program, which offers points for every dollar spent, redeemable for free pizzas and sides. This reward structure not only increases repeat visits but also boosts average order value.
Another important behavioral group is occasional users, who turn to Pizza Hut for special occasions like birthdays, movie nights, or sporting events. For this segment, Pizza Hut emphasizes value bundles (like the Big Dinner Box) and limited-time offerings that create urgency. The emotional messaging here focuses on shared experiences and indulgence, aligning with these consumers’ mindset during leisure moments.
Pizza Hut also tailors experiences for first-time or lapsed users, often deploying discount codes or free delivery offers through digital channels to draw them back in. These promotions are strategically personalized using data analytics and user browsing behavior, especially through the app and website.
Furthermore, Pizza Hut uses purchase data to upsell products. For instance, customers who frequently order pepperoni pizzas may be shown spicy or stuffed crust options, while dessert purchasers might see ads for new sweet menu items. This behavior-driven personalization enhances the relevance of each interaction.
By analyzing purchase frequency, spending habits, and promo responsiveness, Pizza Hut ensures that its marketing and digital experiences feel personal, timely, and rewarding—key to staying competitive in the delivery-first dining economy.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation categorizes consumers based on their values, lifestyle, personality traits, and emotional motivations. Unlike demographic or behavioral data, psychographics dive deeper into why people buy, revealing the emotional and psychological triggers behind customer choices. For Pizza Hut, this approach is vital to building long-term brand affinity and emotional relevance.
One of the primary psychographic profiles Pizza Hut targets is the family-first lifestyle. These consumers value togetherness, reliability, and affordability. Pizza Hut’s branding—often featuring family gatherings, birthday parties, or movie nights—taps into these moments of connection. Messaging like “Bring the family together” or “Dinner made easy” emphasizes the emotional relief and bonding the brand facilitates.
Pizza Hut also appeals to young, convenience-driven consumers who value freedom, minimal effort, and instant gratification. These customers often balance fast-paced work or school schedules and see food delivery as an extension of personal time management. By highlighting quick delivery, mobile app usability, and limited-time flavor drops, Pizza Hut connects with this group’s preference for low-effort indulgence.
Another psychographic target includes consumers drawn to nostalgia and brand familiarity. Pizza Hut leans into its decades-long history, particularly in regions like the U.S., where people remember dine-in visits from childhood. Campaigns featuring retro logos, the return of the “Big New Yorker,” or the revival of dine-in aesthetics play directly to this emotional connection.
Globally, Pizza Hut also attracts customers who value Western-style dining as aspirational. In emerging markets, eating at Pizza Hut can symbolize modernity or status. For this group, the brand enhances its appeal through stylish interiors, menu adaptations, and premium packaging, aligning with a lifestyle that prizes upward mobility and global identity.
Whether appealing to busy parents, nostalgic millennials, or young urban dreamers, Pizza Hut’s psychographic strategy is about more than selling pizza—it’s about selling experiences, emotions, and identity.
Pizza Hut Marketing Strategy
Pizza Hut’s marketing strategy blends mass appeal with localized personalization, allowing it to connect with a global audience while remaining relevant in each market. The brand uses a mix of traditional advertising, digital engagement, social media, influencer partnerships, and app-based promotions to reach its audience effectively.
The core message across most markets emphasizes convenience, affordability, and enjoyment. In the U.S., campaigns like “No One OutPizzas the Hut” highlight Pizza Hut’s legacy and confidence in product quality. Internationally, the brand often adapts its messaging to match cultural nuances—for example, promoting communal dining in Asia or indulgence during celebrations in the Middle East.
Social media plays a central role in Pizza Hut’s outreach. The brand maintains a presence across platforms like Instagram, TikTok, Facebook, and YouTube, where it showcases new menu items, memes, behind-the-scenes content, and user-generated posts. This helps keep the brand top-of-mind for young digital natives.
Pizza Hut also invests in sports and entertainment partnerships, such as being the official pizza sponsor of the NFL. These tie-ins help reinforce the brand as the go-to option for group dining during televised events.
Ultimately, Pizza Hut’s marketing strategy is about staying accessible and culturally attuned, using humor, emotional connection, and convenience to retain loyal customers while attracting new ones.
How Pizza Hut Reaches Its Audience
Pizza Hut employs a variety of tailored channels to engage different segments of its audience, each designed to meet customers where they are and speak to their specific needs and values.
In‑App and Online Ordering
Pizza Hut’s mobile app and website serve as major audience touchpoints. Frequent users—particularly young professionals and students—make use of loyalty rewards, personalized deals, and one-click reordering. The platform’s data-driven recommendations and promo notifications keep customers engaged and increase average order value.
Takeout and Delivery Partnerships
Pizza Hut collaborates with third-party delivery services like Uber Eats and DoorDash (in markets like the U.S.) to expand reach. These partnerships cater to convenience-driven consumers who prefer ordering through familiar platforms. Pizza Hut maintains its own delivery fleet in many locations to control customer experience and quality.
Social Media and Influencer Campaigns
Targeting younger demographics and nostalgia-seeking adults, Pizza Hut uses platforms like Instagram, TikTok, Facebook, and YouTube to showcase new flavors, retro campaigns, and behind-the-scenes content. Influencer partnerships—such as food bloggers or local celebrities—are used to introduce limited-time pizzas or country-specific styles, reinforcing local relevance and cultural resonance.
Television, Sports, and Event Sponsorship
Traditional advertising remains an important component, especially for family audiences and regional awareness. TV commercials during prime time or sports broadcasts emphasize Pizza Hut’s legacy. Sponsorships—such as the NFL partnership in the U.S.—anchor the brand in communal experiences like game nights, positioning Pizza Hut as the go‑to option for gatherings.
Local Promotions and Community Engagement
In many countries, Pizza Hut tailors local marketing campaigns—such as community festivals or themed promotions (family nights, student specials)—to create grassroots visibility. These localized efforts help the brand adapt to specific neighborhoods, shopping malls, or university campuses, reinforcing its presence in everyday life.
By combining digital personalization with mass messaging and local activation, Pizza Hut ensures each customer segment receives messages that align with their behaviors, values, and preferred channels.
Comparison to Competitors’ Target Audience
To better understand how Pizza Hut positions itself in the global pizza market, it’s essential to compare its target audience with two major competitors: Domino’s Pizza and Papa John’s. Each brand has cultivated a distinct identity and audience, though overlaps exist.
Pizza Hut vs Domino’s Target Audience
Both Pizza Hut and Domino’s aim for a similar mass-market demographic, but they diverge in how they define convenience and customer experience. Domino’s primarily targets young adults and working professionals, leaning heavily into tech-driven ordering and delivery innovation. Its mobile-first approach and quick delivery appeal to a highly digital, efficiency-seeking customer base.
Pizza Hut, in contrast, retains a stronger appeal to families and nostalgia-driven consumers, especially in the U.S. The brand emphasizes comfort, tradition, and menu variety, including pasta, wings, and desserts. While Domino’s promotes speed and price transparency, Pizza Hut plays up value through combo meals and large-format deals like the Big Dinner Box.
Internationally, Domino’s often focuses on urban centers and high-density zones, leveraging its logistical infrastructure for 30-minute delivery promises. Pizza Hut, while also active in cities, maintains more dine-in formats abroad, catering to communal dining habits and status-driven consumer behavior.
Pizza Hut vs Papa John’s Target Audience
Papa John’s tends to target a slightly more upscale and quality-conscious consumer. Its branding emphasizes ingredients—“Better Ingredients, Better Pizza”—and appeals to customers who perceive food as an extension of lifestyle choices. The audience often includes middle- to upper-income individuals, including young families and health-aware professionals.
Pizza Hut, by contrast, does not place the same spotlight on premium ingredients. Instead, it emphasizes quantity, variety, and familiarity. This positions it as a more casual and accessible brand, with broader appeal across income levels. While Papa John’s might attract customers with artisanal preferences, Pizza Hut wins with indulgent flavors, creative crusts, and value-centric promotions.
Similarities in Target Audiences
All three brands serve customers who want quick, affordable, and flavorful meals. Young adults (18–34) are a shared core across the board, especially for digital ordering and late-night delivery. All offer loyalty programs and app-based experiences that tap into modern convenience-driven habits. Families, particularly those with children, remain an important target for all three, especially during weekends and holidays.
Key Differences in Target Audiences
The most notable difference lies in emotional branding. Pizza Hut leans into nostalgia and togetherness; Domino’s emphasizes speed, tech, and reliability; Papa John’s stresses quality and ingredient transparency. These distinctions help each brand build specific emotional connections—Pizza Hut with tradition, Domino’s with innovation, and Papa John’s with food credibility.
Another key difference is in regional strategy. Domino’s dominates in densely populated urban areas with minimal dine-in focus. Pizza Hut, by contrast, maintains a mix of dine-in, takeout, and delivery, especially in Asia and the Middle East. Papa John’s focuses its efforts more on premium positioning, often limiting its appeal to a narrower demographic.
Pizza Hut Advantages
- Broad Menu Customization
Pizza Hut’s diverse menu appeals to multiple dietary needs and taste preferences. From stuffed crusts to vegetarian and international flavors, this adaptability allows it to attract a wider audience than more specialized competitors. - Global Footprint with Local Flavor
With over 18,000 locations worldwide, Pizza Hut excels at localizing its menu. Whether offering chicken tikka pizza in India or shrimp toppings in Thailand, this flexibility boosts regional relevance and brand loyalty. - Legacy and Emotional Loyalty
Pizza Hut has decades of brand equity, especially in markets like the U.S. Many consumers associate the brand with childhood or family dinners, giving it a nostalgic edge that competitors lack. - Multi-Channel Presence
Pizza Hut’s presence across dine-in, delivery, and takeout formats ensures it can serve a wider variety of customer scenarios, from casual dining to on-the-go meals.
Pizza Hut Disadvantages
- Slower Tech Adoption Compared to Domino’s
While Pizza Hut has improved its digital presence, Domino’s still leads in tech innovation—especially in delivery tracking, GPS driver updates, and order automation. This puts Pizza Hut at a disadvantage among younger, tech-first consumers. - Perceived as Less Premium Than Papa John’s
Pizza Hut’s value-based branding may alienate consumers who associate quality with higher-end ingredients. Papa John’s “Better Ingredients” narrative captures health-conscious and ingredient-aware diners more effectively. - Dine-In Format Limits Scalability in Urban Centers
In densely populated cities where real estate is expensive, Pizza Hut’s historic investment in dine-in locations is less efficient than Domino’s smaller, delivery-focused footprint. This reduces its urban competitiveness in fast-growth zones. - Inconsistent Global Messaging
Pizza Hut adapts locally, but this can sometimes lead to diluted global branding. While Domino’s has a consistent digital-first identity, Pizza Hut’s message may vary too widely between markets, weakening global brand cohesion.
Conclusion
Understanding the Pizza Hut target market reveals why the brand has maintained its global presence for over six decades. By effectively segmenting its audience—demographically, geographically, behaviorally, and psychographically—Pizza Hut tailors experiences that resonate across cultures and age groups. Whether serving a busy family in suburban America or a student ordering late-night delivery in India, Pizza Hut adapts its offerings with precision.
Its marketing success lies in the ability to balance legacy and innovation. While the brand leans on emotional loyalty and tradition, it also responds to modern demands through digital convenience and localized promotions. Compared to competitors like Domino’s and Papa John’s, Pizza Hut stakes its identity on broad appeal, global customization, and communal experiences.
Yet, to remain competitive, Pizza Hut must continue evolving—closing its technology gap, unifying global branding, and staying aligned with health-conscious trends. As consumer expectations shift, brands that deeply understand and reflect their audience’s evolving lifestyles will lead the market.
In this context, Pizza Hut’s ongoing ability to connect meaningfully with its segmented audience remains a key pillar of its brand strength—and a model for businesses navigating the complexities of global marketing.







