Burger King Target Market Analysis
Understanding a company’s target market is essential to building a successful brand. It shapes product offerings, marketing strategies, and the customer experience. For fast food chains, which operate in a highly competitive and dynamic space, knowing precisely who their core customers are can make or break market share.
Burger King, one of the world’s largest fast-food chains, operates in over 100 countries and serves millions daily. Known for its flame-grilled burgers and cheeky advertising campaigns, the brand has carved a distinct identity within the quick-service restaurant (QSR) industry. But behind its playful exterior lies a deeply strategic approach to audience engagement.
In this article, we’ll explore the Burger King target market in depth. We’ll examine who they serve, how they segment their audience, and what sets them apart from competitors like McDonald’s and Wendy’s. Through demographic, geographic, behavioral, and psychographic lenses, we’ll break down how Burger King attracts its audience and adapts to market demands. Finally, we’ll compare Burger King‘s strategy with rivals and assess its competitive advantages and challenges.
Contents
Who is Burger King’s Target Audience?
The Burger King target market primarily consists of young adults and middle-income families looking for affordable, quick, and satisfying meals. These customers are typically aged 18 to 35, with a significant portion falling into the millennial and Gen Z demographics. While the brand appeals to a broad audience, its tone and campaigns are often tailored to resonate with a younger, digitally native crowd.
Burger King customers are often value-conscious but still seek quality and customization. Many are drawn to the brand’s flame-grilled cooking method, a point of differentiation from competitors like McDonald’s. Income-wise, most consumers fall within the lower-middle to middle-income brackets, often earning between $30,000 and $70,000 annually. These customers seek meals that balance affordability with taste and convenience.
Behaviorally, Burger King’s audience includes frequent fast-food diners who appreciate quick service, mobile ordering, and limited-time promotions. The brand’s loyalty programs and app-based deals also cater to users who enjoy gamified savings and exclusive offers. An example is the “1-Cent Whopper” campaign, where users had to be near a McDonald’s to unlock the deal via the Burger King app—blending humor with mobile engagement.
Culturally, Burger King appeals to those who appreciate boldness and irreverence in branding. The company has taken public stances on social issues and used humor to challenge competitors. This resonates with younger audiences who value authenticity and aren’t afraid to align with brands that have a voice.
Burger King Target Market Segmentation and Marketing
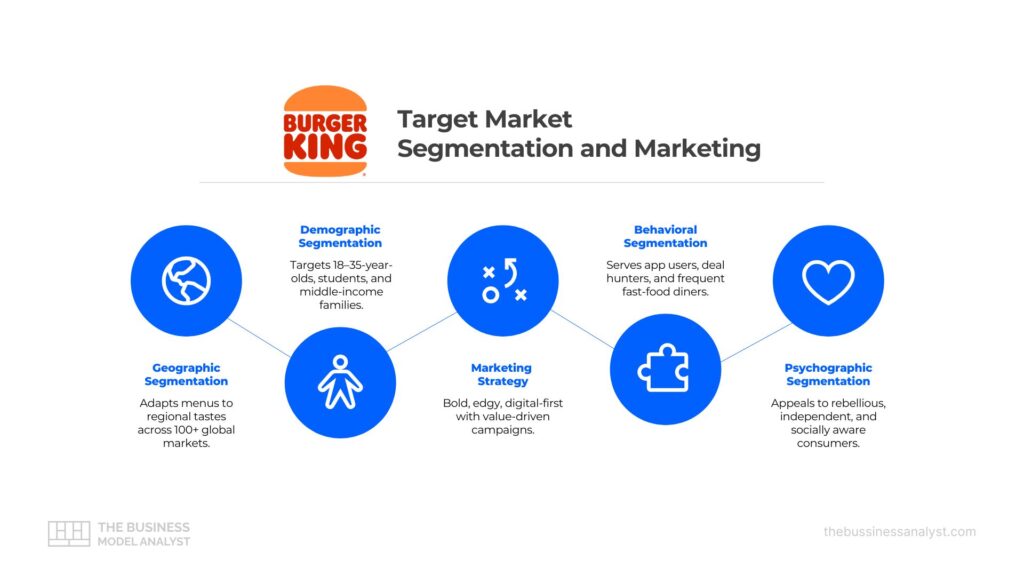
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer base into smaller groups with shared characteristics. This enables brands to craft messages, products, and campaigns that resonate more deeply with specific audience segments. For a global fast-food brand like Burger King, segmentation is vital to remaining competitive and relevant across markets.
Burger King uses segmentation to tailor its marketing and product strategy to various consumer types, optimizing reach and relevance. By analyzing different customer profiles, the brand can adapt its menu, pricing, and tone of voice to better serve specific needs, whether it’s value-focused urban youth or convenience-seeking suburban families.
Burger King employs four main types of segmentation:
- Demographic segmentation to target consumers by age, income, and education
- Geographic segmentation to adjust offerings by region and culture
- Behavioral segmentation to reflect purchasing habits and brand loyalty
- Psychographic segmentation to connect with customer values, attitudes, and lifestyles
Each of these plays a critical role in how Burger King positions itself and interacts with its target market. In the following sections, we’ll break down each segmentation type in detail and explore how Burger King uses them to drive engagement and growth.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is one of the most straightforward yet powerful tools for understanding a brand’s target market. It involves grouping customers based on variables such as age, gender, income, education, and family structure. Burger King’s target market is sharply focused through this lens, particularly around age and income.
The core demographic for Burger King includes men and women aged 18 to 35. This group often includes college students, young professionals, and early-stage families, all of whom value convenience, affordability, and satisfying food. Burger King’s marketing—like humorous ads on YouTube or memes on Twitter—is clearly shaped to attract a younger, internet-savvy crowd.
Income is another key factor. Burger King appeals largely to individuals and families within the lower-middle to middle-income range, roughly between $30,000 and $70,000 annually. These consumers prioritize budget-friendly dining without sacrificing flavor or experience. Burger King’s frequent use of value meals, combo deals, and app-exclusive coupons directly targets this cost-conscious segment.
Education and occupation also play roles. Many customers have some college education or are employed in retail, service, or office jobs. This demographic frequently dines out due to limited time or resources to cook at home, especially during lunch breaks or late nights.
By crafting campaigns like the “2 for $6” deal or emphasizing app discounts, Burger King uses demographic insights to shape both messaging and pricing. This segmentation influences everything from product design—like the compact, budget-friendly Chicken Jr.—to tone of voice, which is irreverent and youthful.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides the market based on physical location, such as country, region, climate, or urban vs. rural setting. For a global brand like Burger King, this type of segmentation is essential for adapting to regional tastes, economic conditions, and cultural preferences.
Burger King operates in over 100 countries, with a particularly strong presence in the United States, Latin America, Europe, and Asia. Each market presents different consumer behaviors and dietary preferences. In the U.S., where Burger King originated, it tailors its menu to American tastes with items like the Whopper, Chicken Fries, and plant-based Impossible Whopper. Meanwhile, in India, where beef consumption is limited due to cultural and religious reasons, Burger King offers vegetarian-friendly options like the Paneer King and Tandoor Grill burgers.
The company also differentiates based on urban vs. suburban locations. Urban locations often offer smaller store formats and emphasize fast service or delivery, while suburban outlets may include larger seating areas and drive-thru lanes to cater to families and commuters.
Even pricing can vary geographically. In economically sensitive regions, Burger King leans into value pricing, while in wealthier urban centers, it introduces premium items or limited-time offers to drive interest and boost margins.
A good example is how Burger King Brazil released region-specific sandwiches inspired by local flavors—like the “Picanha BBQ Burger.” These geographic customizations allow the brand to stay relevant while honoring local food culture.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on the decisions consumers make—how often they buy, what they buy, and why they choose certain brands. For Burger King, these patterns are essential in shaping promotions, loyalty programs, and even the design of digital experiences.
The Burger King target market includes frequent fast-food consumers who value speed, convenience, and consistency. Many of these customers are on-the-go eaters—commuters, students, or late-night diners. Burger King’s mobile app and drive-thru experience are streamlined to appeal to these behaviors. For instance, app users can customize meals, track rewards, and access deals that aren’t available in-store, incentivizing repeat visits.
The brand also focuses on purchase behavior tied to deals and exclusivity. Campaigns like “Whopper Detour,” where customers received a Whopper for one cent if they ordered near a McDonald’s, gamify the purchase experience and create viral buzz. These initiatives not only reward loyalty but drive digital engagement and media coverage.
Burger King’s behavioral segmentation also includes seasonal and trend-based buying. Limited-time offerings, such as Ghost Pepper Chicken Fries during Halloween, tap into consumers’ interest in novelty and social sharing. This short-term excitement boosts foot traffic and app downloads, especially among Gen Z and millennials who enjoy being first to try something new.
Additionally, loyalty is cultivated through the Royal Perks program, which offers points for every purchase. These can be redeemed for free items, encouraging frequent visits. The brand leverages data from this program to understand preferences, push personalized offers, and build long-term customer relationships.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation goes beyond demographics and behaviors, focusing on the values, lifestyles, attitudes, and personalities that influence consumer decisions. For Burger King, this form of segmentation is especially powerful, as the brand leans heavily on emotional appeal, identity, and social relevance.
Burger King primarily attracts young, socially aware, and digitally active consumers who appreciate bold messaging and humor. The brand’s identity is unapologetic, rebellious, and sometimes controversial—traits that resonate with Gen Z and millennials who admire authenticity and cultural commentary. For example, Burger King’s “Moldy Whopper” campaign, which showcased a decaying burger to promote its preservative-free ingredients, appealed to health-conscious and transparency-driven customers who value honesty over traditional food aesthetics.
A key emotional driver for Burger King’s audience is individuality. Unlike McDonald’s, which often emphasizes family and nostalgia, Burger King’s tone suggests: “Be your own king.” This connects with consumers who seek personal choice, independence, and self-expression. The brand reinforces this through its product customization and playful slogan, “Have It Your Way.”
Lifestyle alignment is also clear in how Burger King speaks to tech-savvy, mobile-first eaters. Its digital-first campaigns—like those activated through app geolocation or augmented reality—show the brand understands its audience’s day-to-day life. Many of these customers are multitaskers, juggling work, school, or social obligations, and expect on-demand convenience blended with humor and relatability.
In summary, Burger King taps into a psychographic profile defined by boldness, curiosity, and a demand for brands that feel real, fun, and culturally in-tune. This segmentation helps Burger King cultivate strong emotional bonds and viral brand moments.
Burger King Marketing Strategy
Burger King’s marketing strategy is built around bold creativity, digital innovation, and value-focused messaging. The brand thrives on pushing boundaries, often launching campaigns that are humorous, provocative, or culturally sharp. These campaigns serve not just to promote products but to spark conversations and deepen emotional ties with its audience.
Burger King leans heavily into digital marketing, with a strong presence on platforms like Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok. It uses these channels to engage young consumers with memes, witty responses, and interactive content. At the same time, the brand maintains traditional advertising through TV spots and billboards, especially for national promotions like the “2 for $6” mix-and-match deal.
Influencers and celebrities also play a role. Collaborations with figures like rapper Lil Yachty and Twitch streamers target niche fanbases and younger demographics. Burger King’s messaging often carries a tone of rebellion and humor, using campaigns like “The Whopper Detour” or “Burn That Ad” to attract attention while delivering value.
The core message remains focused on personal choice, flame-grilled quality, and affordability. Whether through mobile coupons or limited-time items, Burger King balances emotional appeal with tangible value, all while reinforcing its identity as the fast-food brand that’s not afraid to stand out.
How Burger King Reaches Its Audience
Burger King utilizes a combination of digital, in-store, out-of-home, and partnership-driven marketing to target specific audience segments effectively. Each method is optimized to match the preferences and lifestyles uncovered through its segmentation strategy.
Digital & Social Media
Burger King leverages platforms like Twitter, TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube to reach younger, digitally native audiences. By posting humorous content, memes, and quick-response commentary on trending topics, it connects with Gen Z and millennials in real time. These channels help amplify viral campaigns and keep the brand culturally current.
Mobile App & Loyalty Channels
The Burger King mobile app, including its Royal Perks loyalty program, is central to behavioral engagement. It offers location-based deals (e.g. Whopper unlocks near competitors), personalized offers, and gamified promotions. This approach encourages frequent visits and app engagement through convenience and exclusive rewards.
In-Store & Drive-Thru Experience
For customers on the go—commuters, families, students—Burger King invests in optimizing its drive-thru and in-store systems. Efficient ordering kiosks, digital menu boards, and streamlined layouts improve service speed. These features align with Burger King’s behavioral segment of value-seeking, time-pressed diners.
Out-of-Home & Traditional Ads
While digital is primary, Burger King still runs TV commercials, billboards, and outdoor displays for major campaigns. These ads amplify flagship promotions (like “2 for $6” combos) and support image-building around flame-grilled quality and bold brand voice. Such broad media reach reinforces brand identity across broader demographics.
Partnerships & Influencer Campaigns
Burger King collaborates with influencers, micro-celebrities, and pop culture figures to engage niche but enthusiastic fan segments. Whether partnering with Twitch streamers or rapper-sponsored specials, these collaborations build relevance within youth culture and social media-savvy consumers.
By weaving these channels together, Burger King ensures each target segment is reached through formats that resonate—humor and viral potential for younger digital users; deals and rewards for value-driven patrons; efficient service for time-conscious customers.
Comparison to Competitors’ Target Audience
Burger King vs McDonald’s Target Audience
Burger King and McDonald’s target similar demographic groups—primarily young adults, students, and middle-income families. Both brands attract customers aged roughly 18–35, with strong appeal to those seeking value and speed. However, McDonald’s often emphasizes family-friendly messaging and comfort food nostalgia, while Burger King leans into irreverence and personalization. McDonald’s also has deeper penetration in rural and suburban markets thanks to its larger footprint. In contrast, Burger King cultivates loyalty among digitally active, urban consumers who prefer bold, differentiated brand identity.
Burger King vs Wendy’s Target Audience (optional)
Wendy’s similarly targets millennial and Gen Z customers seeking quality fast food. Where Burger King promotes authenticity through flame-grilling and customization, Wendy’s emphasizes freshness, premium ingredients, and transparency (e.g., “never frozen” beef). Wendy’s branding skews witty and candid, but less edgy than Burger King. Geographic focus also differs: Wendy’s heavily pursues U.S. college towns and suburban chains, while Burger King maintains broader international reach with regionally localized menu items.
Similarities in Target Audiences
Both Burger King and its competitors share core audience traits: young adults, students, and budget-conscious families who value convenience, digital ordering, and fast, tasty meals. They engage regularly with mobile apps, loyalty programs, and seasonal or promotional offerings. Across brands, there is strong overlap in psychographics—consumers who prefer bold flavors, social sharing, and brand personality—though the tone may vary.
Key Differences in Target Audiences
Burger King’s strategy leans more toward urban, digitally engaged individuals who respond to cultural irreverence and excitement. McDonald’s plays heavily to broader, multi-generational and family-based audiences. Wendy’s targets a similar age group but emphasizes quality, transparency, and regional familiarity. Burger King’s tone is more activist or provocative, which can alienate some segments that prefer consistent, comforting experiences.
Burger King Advantages
- Brand Boldness & Cultural Relevance
Burger King’s edgy campaigns—such as “Moldy Whopper” and competitor-driven promotions—create strong attention and emotional connection with younger audiences. This helps the brand stay culturally relevant and shareable. - Global Reach with Local Adaptation
Operating in dozens of countries, Burger King adeptly introduces region-specific menu items (e.g. Paneer King in India, Picanha Burger in Brazil). This flexibility deepens relevance across diverse geographic segments. - Digital-First Engagement Model
With innovations like app-based Whopper Detour and loyalty gamification, Burger King strengthens behavioral engagement and drives repeat visits through data-driven personalization and mobile convenience. - Personalization & Customization
The “Have It Your Way” positioning empowers consumers to personalize orders. Combined with transparent ingredient campaigns, this builds trust and highlights choice—key for audiences valuing autonomy and authenticity.
Burger King Disadvantages
- Less Uniform Family Appeal
Unlike McDonald’s, Burger King’s rebellious tone and edgy marketing sometimes alienate older or family-oriented consumers who prefer comforting, multi-generational brand cues. - Smaller U.S. Footprint vs McDonald’s
While strong internationally, Burger King often has fewer outlets per capita in many U.S. suburbs and rural areas, limiting access for non-urban target segments compared to McDonald’s. - Controversial Campaign Risks
Bold, provocative marketing can backfire—Burger King’s activism‑style campaigns may provoke backlash or seem tone-deaf in certain markets. This risk may affect brand perception among conservative or less digitally savvy segments. - Quality Perception Variability
While Wendy’s is widely recognized for fresh, never‑frozen beef, Burger King’s image fluctuates between flame‑grilled quality and fast‑food compromise. This can put off consumers who prioritize ingredient transparency.
Conclusion
Burger King’s ability to identify, understand, and engage its target market is central to its position in the fast-food landscape. Through a mix of demographic precision, regional customization, behavioral data, and psychographic insights, Burger King crafts a brand that is bold, distinctive, and relevant—especially among younger, digitally engaged audiences.
By leveraging digital channels, mobile app innovation, and culturally savvy marketing, the brand has carved out a space where personalization meets value-driven convenience. Compared to competitors like McDonald’s and Wendy’s, Burger King takes more risks with tone and engagement, offering a sharper, sometimes rebellious identity that resonates with those who crave more than just a meal.
However, Burger King must continuously navigate the fine line between edgy and alienating, and work to solidify perceptions of quality and consistency—especially across diverse global markets.
In a fast-evolving industry where consumer values and behaviors shift rapidly, Burger King’s strength lies in its willingness to adapt, listen, and lead through creative, strategic segmentation. As the brand moves forward, staying in tune with its audience’s expectations will be key to maintaining loyalty and expanding its reach.







