Google Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a strategic tool developed by Michael Porter to examine the series of steps a company uses to deliver a product or service, helping identify where value is created and competitive advantages arise. The model separates activities into primary functions—directly related to production—and support functions that enhance operational efficiency.
Google value chain analysis reveals how the company leverages innovation, data infrastructure, and a vast ecosystem of services to maximize profitability and scale. From its search engine and advertising platforms to hardware and cloud services, Google refines each component of its operations to reduce costs, boost customer engagement, and drive technological leadership. Through strategic management of both primary and support activities, Google sustains dominance in digital advertising, data processing, and artificial intelligence. This analysis explores the mechanisms behind Google’s operational efficiency and enduring market edge.
Contents
Overview of Google
Founded in 1998 by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google began as a research project at Stanford University and rapidly transformed into the world’s most widely used search engine. Its early innovation—PageRank—redefined how search results were prioritized, setting the stage for rapid growth. Google restructured under the Alphabet Inc. umbrella in 2015, enabling a broader portfolio strategy.
Over the years, Google has expanded far beyond search, diversifying its offerings through acquisitions like YouTube, Android, and Fitbit. Its portfolio now includes cloud computing, smart home products, and AI-driven tools, making it a technology conglomerate with global reach. The Google business model integrates advertising revenue, hardware sales, subscriptions, and enterprise services, all supported by data analytics and machine learning. This multi-channel structure reflects many of the patterns seen in different revenue streams across digital-first companies.This diverse approach has allowed Google to remain adaptive and profitable in an evolving digital landscape.
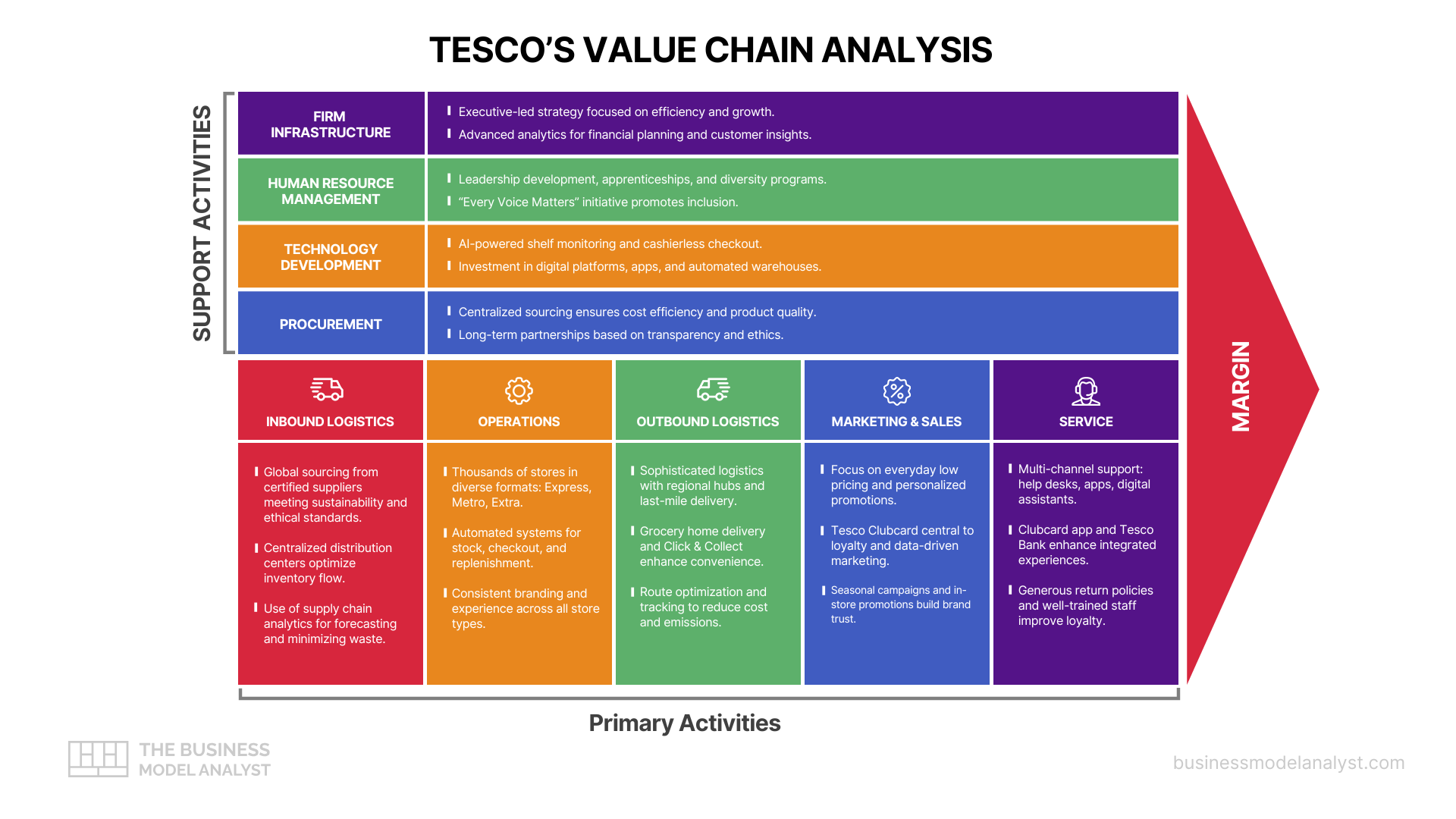
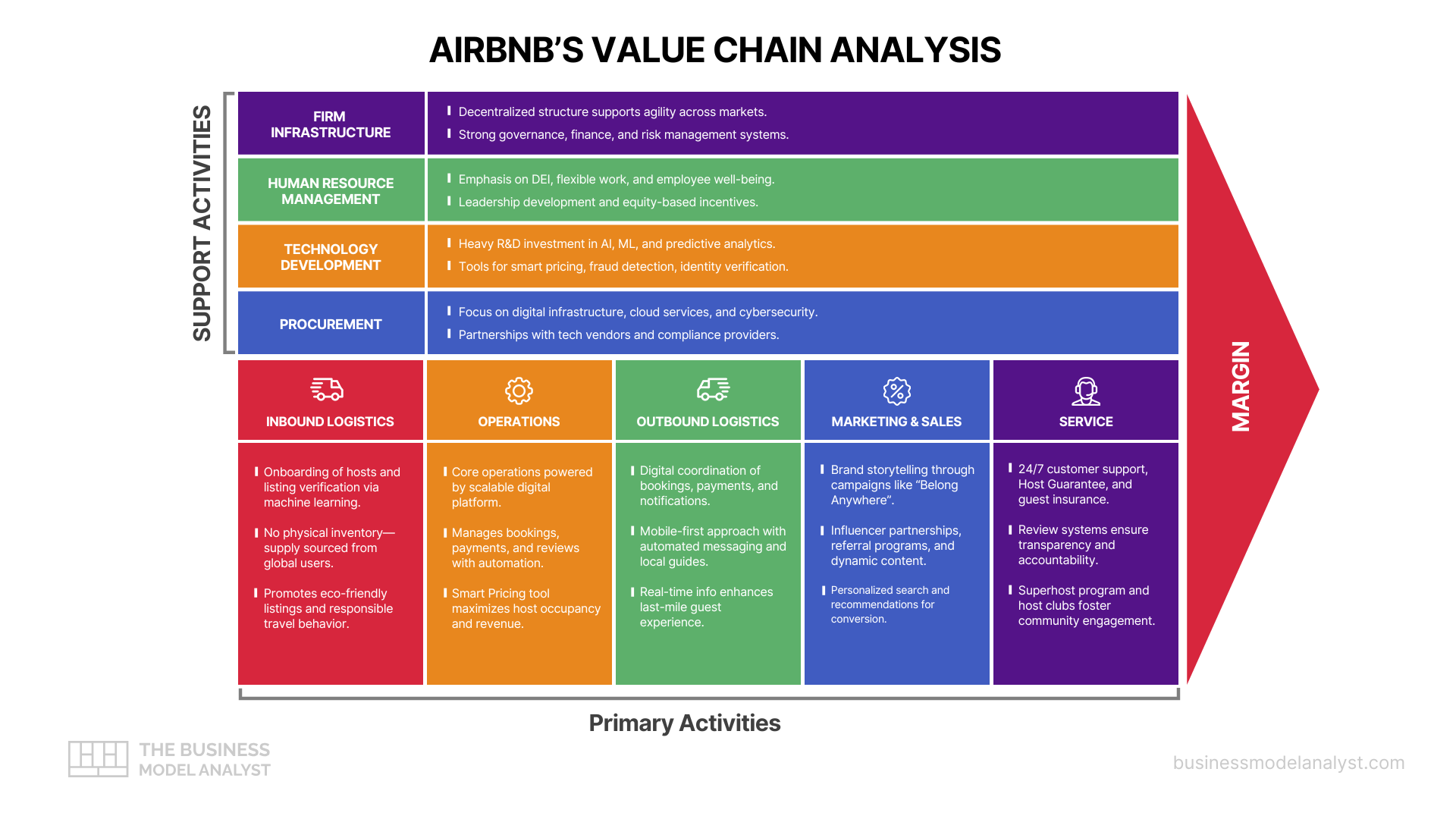
Primary Activities in Google Value Chain
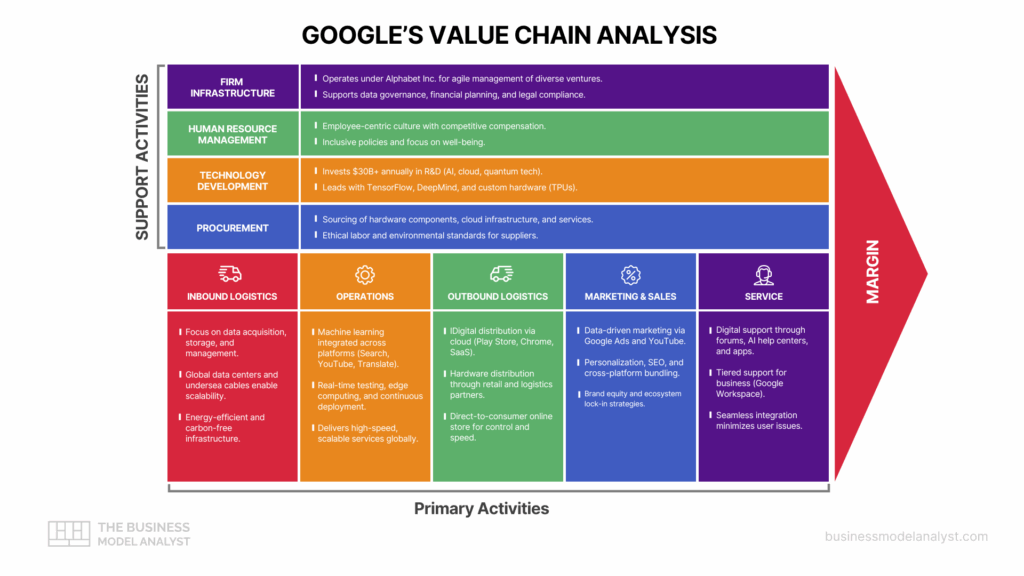
Inbound Logistics
Google’s inbound logistics center on data acquisition, storage, and management. With global data centers and undersea cables, it efficiently collects and processes vast volumes of data from web activity, devices, and partnerships. The company prioritizes energy-efficient infrastructure, aiming for carbon-free energy 24/7. Strategic data sourcing and advanced cooling systems contribute to operational sustainability and long-term cost control — both critical factors when analyzing a company’s key resources.
Operations
Google’s operations revolve around its cloud platforms, search engine algorithms, and AI services — all of which are tightly linked to its core key activities that sustain growth and user retention. The company employs advanced machine learning across all product lines—from Google Search to YouTube and Google Translate—improving functionality and personalization. Continuous deployment, real-time testing, and edge computing help Google deliver services with high speed and uptime, ensuring global scalability and quality.
Outbound Logistics
Google’s products and services are primarily digital, allowing instant global distribution. Its Play Store, Chrome updates, and SaaS solutions reach users seamlessly via cloud infrastructure. For hardware like Pixel phones and Nest devices, Google partners with logistics providers and retail outlets to ensure timely distribution. Its direct-to-consumer model and online store enhance delivery speed and user control.
Marketing and Sales
Google uses data-driven marketing through its own advertising tools like Google Ads and YouTube. Personalization, search engine optimization (SEO), and cross-platform integration strengthen outreach. The company leverages brand equity, partnerships, and product ecosystem lock-in—like bundling services with Android or Gmail—to drive user engagement and loyalty while minimizing acquisition costs.
Service
Google maintains extensive digital support via forums, AI-powered help centers, and premium assistance for business clients. Products like Google Workspace come with tiered customer support, while consumer services offer seamless integration and intuitive design to minimize issues. Frequent updates and bug fixes further reinforce service quality and user retention.
Support Activities in Google Value Chain
Firm Infrastructure
Google operates under Alphabet Inc., which allows it to manage diverse ventures with agility. Its infrastructure supports data governance, financial planning, legal compliance, and corporate social responsibility. Google emphasizes environmental stewardship, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2030. This strategic governance model fosters innovation while maintaining accountability and long-term vision.
Human Resource Management
Google is known for its employee-centric culture. The company invests heavily in attracting top talent through competitive compensation, inclusive policies, and a focus on well-being. Programs for continuous learning, career development, and diversity (like its DEI initiatives) ensure a dynamic workforce that supports innovation and cross-functional collaboration globally. People strategy, in this context, becomes one of Google’s most important customer relationship assets.
Technology Development
At its core, Google thrives on innovation. It invests over $30 billion annually in R&D, driving advances in AI, cloud computing, and quantum technology. Tools like TensorFlow, DeepMind breakthroughs, and custom hardware (like TPUs) showcase its leadership. These technologies improve product performance, user experience, and provide scalable enterprise solutions.
Procurement
Google’s procurement involves sourcing hardware components, cloud infrastructure materials, and third-party services. It manages supplier relationships through rigorous standards for ethical labor and environmental impact. For hardware production, Google partners with vetted manufacturers and chip designers, ensuring consistent quality, security, and cost efficiency across its ecosystem.
Analysis of Google’s Competitive Advantage
Google’s value chain reinforces its dominant market position through a blend of innovation, scalability, and customer-centric strategies. Its mastery of primary activities—particularly in operations and outbound logistics—enables rapid, reliable digital service delivery to billions. Seamless integration between services (like Search, Maps, and Gmail) increases user stickiness and ecosystem dependence.
On the support side, Google’s commitment to technology development ensures it remains ahead in fields like AI, machine learning, and cloud services. Its robust infrastructure and agile firm structure allow for bold investments and quick pivots, maintaining relevance across industries. Talent management further enhances this adaptability, with diverse teams fueling innovation.
By aligning procurement, sustainability goals, and efficient data infrastructure, Google drives long-term cost efficiency and market resilience. Unlike many rivals, Google combines monetization strength with service ubiquity. This dual edge—advertising revenue scale and global digital infrastructure—anchors its enduring competitive advantage amid evolving tech landscapes.
Key Takeaways from Google Value Chain
Google value chain analysis reveals how strategic integration of core and support activities drives its global success. Primary functions—like data-driven operations, seamless digital logistics, and targeted marketing—maximize reach and efficiency. Complementary support functions, such as cutting-edge R&D and ethical procurement, bolster innovation and sustainability.
Google leverages internal synergies across its platforms to create a sticky ecosystem, reducing user churn and boosting lifetime value — a textbook case of how strategic value proposition design drives both loyalty and differentiation. Its continued investment in AI and infrastructure ensures scalability and relevance. This cohesive structure not only supports profitability but also positions Google to adapt rapidly in a dynamic digital economy.