-
×
Insurtech Business Models
1 × $29 -
×
Business Model Metrics and KPIs
1 × $29 -
×
The Perfect Business Plan
1 × $29 -
×
Cost Models
1 × $29 -
×
Web 3.0 Business Models
1 × $29 -
×
Super Guides Bundle
1 × $97 -
×
LinkedIn Strategies
1 × $19 -
×
Pricing Strategies for Digital Products
1 × $24 -
×
Digital Marketing Agency Management
1 × $24 -
×
Company Vision Statements
1 × $24 -
×
Marketing Automation
1 × $29 -
×
Lead Generation
1 × $29 -
×
Sales Enablement
1 × $29 -
×
Pricing Strategies for Retailers
1 × $29 -
×
Customer Journey
1 × $29 -
×
Cognitive Biases
1 × $29 -
×
OKR Essentials
1 × $29 -
×
Pricing Strategies for Service Providers
1 × $29 -
×
10 Most Profitable Business Models in 2023
1 × $29 -
×
Project Management Frameworks
1 × $29 -
×
Startup Funding Strategies
1 × $29 -
×
Top 100 Venture Capital Firms
1 × $29 -
×
Negotiation Strategies and Techniques
1 × $29 -
×
Hotel Business Models
1 × $29 -
×
Pricing Strategies for SaaS
1 × $29 -
×
Growth Hacking Techniques
1 × $29 -
×
Business Model Evolution
1 × $29 -
×
Business Model Assessment
1 × $29 -
×
Consulting Business Models
1 × $29 -
×
Fintech Business Models
1 × $29 -
×
170+ Business Model Canvas Examples
1 × $0 -
×
Business Model Innovation with ChatGPT
1 × $119 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Childcare and Early Education
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Waste Management and Recycling
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Personal Finance and Wealth Management
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Subscription Products & Services
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Space Technology and Services
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Educational Tech Startups
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Urban Farming
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Flower Shops
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Coffee Shops
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Jewelry Stores
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for 3D Printing Services
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Sustainable Fashion
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Yoga Studios
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Plant-Based Foods and Alternatives
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Bookstores
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Mobile App Development
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Elder Care Services
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Biotechnology
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Renewable Energy Solutions
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Smart Home Technology
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for eSports and Gaming
1 × $49 -
×
10 Innovative Business Models for Drone Technology and Services
1 × $49 -
×
Business Model Canvas SWOT Analysis Assesment Excel Spreadsheet
1 × $97
Pepsico Value Chain Analysis
Value chain analysis is a strategic tool introduced by Michael Porter to identify the internal activities through which a company adds value to its products or services. It distinguishes between primary activities—those directly related to production and delivery—and support activities that enable or enhance them. This framework helps assess how businesses gain competitive advantage and boost profitability.
PepsiCo value chain analysis reveals how the company leverages its global scale and diversified portfolio to drive operational efficiency and maximize returns. By closely managing each step—from sourcing raw materials to customer service—PepsiCo ensures consistent product quality, swift distribution, and strong brand presence. Its value chain highlights not only cost-effectiveness but also responsiveness to changing consumer trends and sustainability goals.
Contents
Overview of PepsiCo
Founded in 1965 through the merger of Pepsi-Cola and Frito-Lay, PepsiCo has evolved into one of the world’s leading food and beverage companies. Headquartered in Purchase, New York, it operates in over 200 countries, offering a diverse portfolio that includes iconic brands such as Pepsi, Lay’s, Gatorade, Tropicana, and Quaker.
PepsiCo’s growth strategy includes innovation, global expansion, and strategic acquisitions. Milestones like acquiring Tropicana in 1998 and SodaStream in 2018 illustrate how it has diversified into health-conscious and eco-friendly segments. The company has also rebranded to emphasize sustainability and inclusivity.
The PepsiCo business model is built on delivering convenient foods and beverages through a balanced mix of global scale and local execution. Its integrated supply chain and multi-channel distribution enable consistent product availability while supporting rapid adaptation to regional preferences.
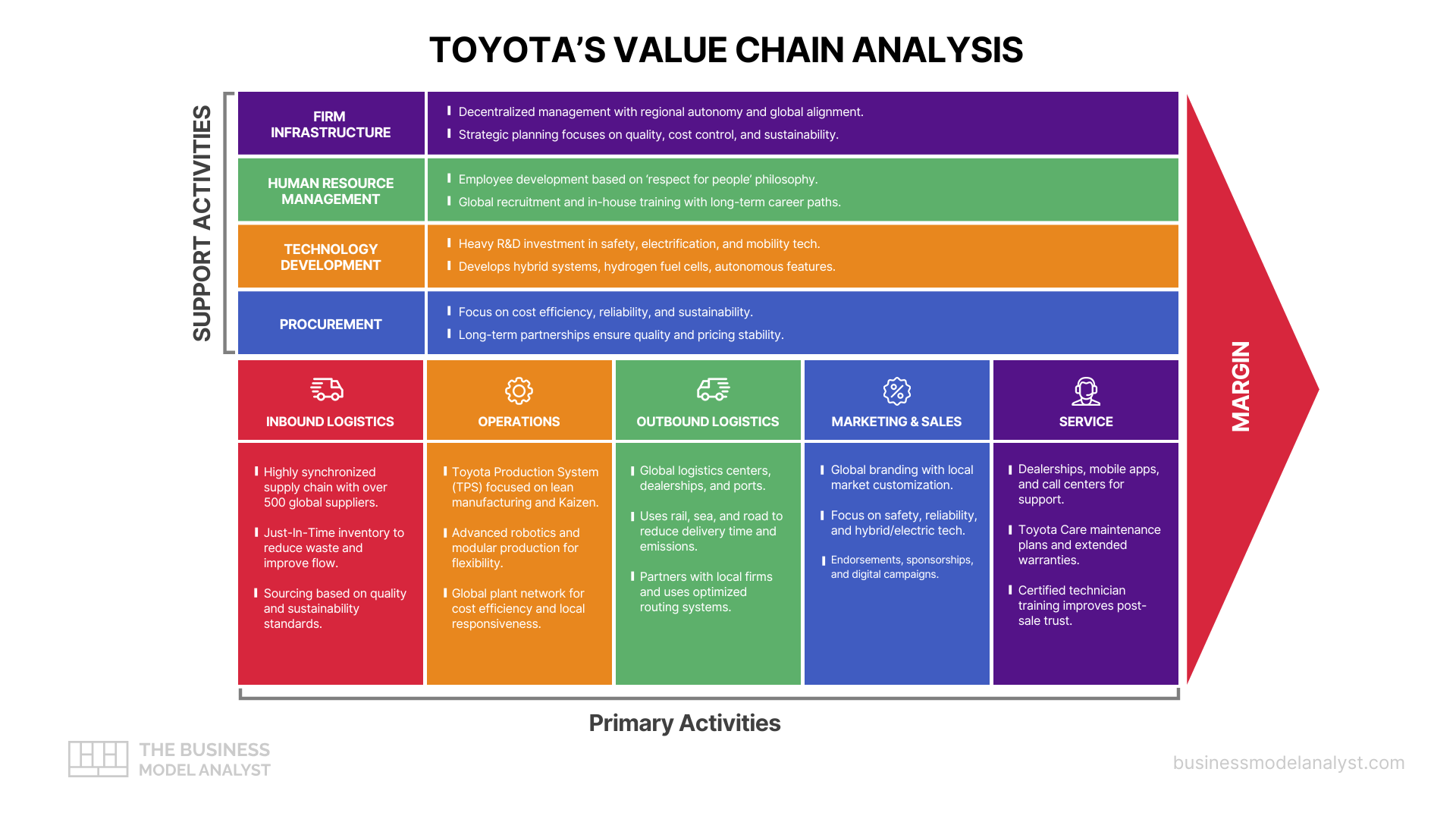
Primary Activities in PepsiCo Value Chain
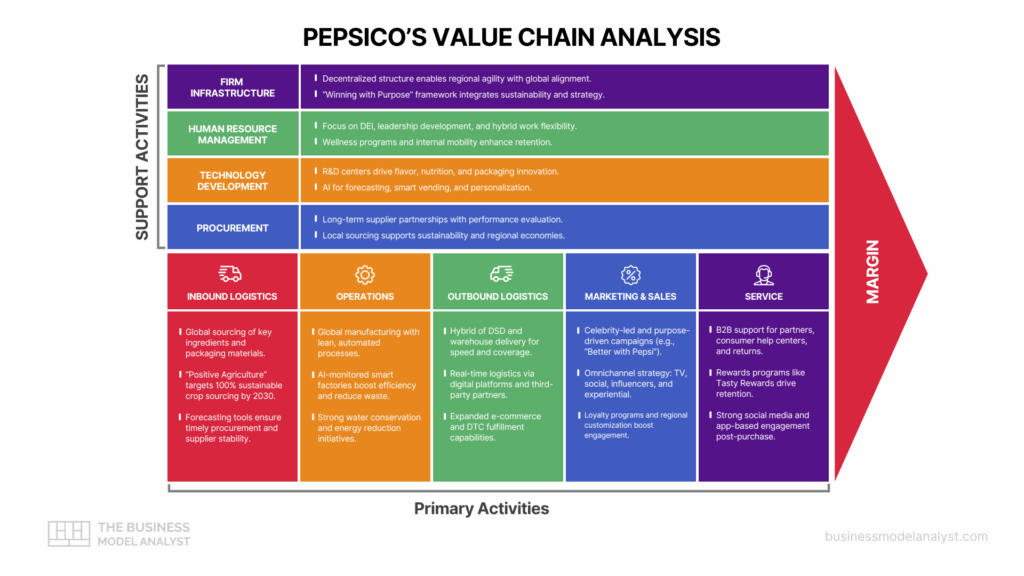
Inbound Logistics
PepsiCo’s inbound logistics involve sourcing raw materials such as corn, potatoes, sugar, and packaging materials from a global network of suppliers. The company emphasizes sustainability, choosing vendors committed to ethical labor practices and environmental stewardship. Its “Positive Agriculture” initiative aims to sustainably source 100% of key crops by 2030, enhancing traceability and reducing emissions.
PepsiCo employs advanced forecasting tools to manage procurement efficiently. These systems anticipate supply needs based on historical data and market trends. Quality control is rigorous, with strict protocols ensuring consistent ingredient standards across production sites. Strategic supplier partnerships also help mitigate risks and stabilize costs.
Through streamlined procurement and sustainable sourcing, PepsiCo reduces delays and waste, strengthening the first link of its value chain.
Operations
PepsiCo operates manufacturing plants globally to process beverages, snacks, and cereals. These facilities utilize lean production methods and automation to optimize output while minimizing waste. High-tech systems manage everything from ingredient mixing to packaging, ensuring precision and product uniformity.
One notable example is its smart factories using AI to monitor energy use and machine performance in real time. This enhances productivity and reduces operational costs. PepsiCo also implements water conservation and waste reduction programs across plants, aligning with its sustainability goals.
Efficient operations allow PepsiCo to meet global demand promptly while maintaining high standards in quality and environmental impact.
Outbound Logistics
PepsiCo’s outbound logistics span a complex network of warehouses, regional distribution centers, and retail channels. Products are delivered through a hybrid model of direct-store-delivery (DSD) and warehouse delivery systems, ensuring broad market reach and quick replenishment cycles.
The company leverages digital supply chain platforms to optimize routing, inventory management, and real-time tracking. Strategic partnerships with third-party logistics firms also enhance speed and flexibility. With growing e-commerce demand, PepsiCo has expanded its digital fulfillment capabilities for both B2B and DTC channels.
This agile distribution infrastructure ensures timely delivery and product availability, critical for consumer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
Marketing and Sales
PepsiCo uses data-driven marketing to personalize consumer engagement across traditional and digital platforms. Its campaigns often feature celebrity endorsements and social issues, building brand relevance. The “Better with Pepsi” and “For the Love of It” campaigns highlight storytelling that reinforces emotional connections.
The company’s omnichannel presence includes TV, social media, influencer marketing, and experiential events. Loyalty programs and dynamic pricing strategies further strengthen customer relationships. Localized advertising caters to regional tastes, enhancing global brand resonance.
By blending emotional branding with analytics, PepsiCo drives customer loyalty, brand differentiation, and sales growth across its diversified portfolio.
Service
PepsiCo prioritizes service excellence through responsive customer support and loyalty-building programs. The company offers dedicated B2B customer service for retailers and foodservice partners, ensuring smooth operations and supply coordination.
For consumers, PepsiCo maintains robust online help centers, easy product returns, and digital engagement via apps and social platforms. Personalized offers and rewards programs like PepsiCo Tasty Rewards foster brand affinity.
Post-sale support and consumer interaction contribute to long-term loyalty and customer retention, reinforcing PepsiCo’s value proposition.
Support Activities in PepsiCo Value Chain
Firm Infrastructure
PepsiCo’s firm infrastructure includes leadership, governance, and performance management systems that align with its strategic goals. The company follows a decentralized structure, empowering regional units to adapt quickly to local market dynamics while maintaining global consistency.
Its strategic planning emphasizes sustainability and long-term growth. Tools like PepsiCo’s “Winning with Purpose” framework integrate corporate responsibility into financial objectives. Strong compliance programs and risk management systems ensure legal and ethical operations across all geographies.
This infrastructure supports operational resilience and strategic agility, which are vital for navigating global complexities and driving sustained value.
Human Resource Management
PepsiCo’s talent strategy focuses on building a diverse, inclusive, and high-performing workforce. The company invests in leadership development, upskilling programs, and internal mobility to enhance employee engagement and retention.
Diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) are central to its HR practices. PepsiCo has set public DEI goals and regularly reports progress. Employee well-being is also prioritized through wellness programs and hybrid work flexibility.
By fostering a supportive and innovative workplace, PepsiCo strengthens organizational culture and attracts top global talent to maintain its competitive edge.
Technology Development
PepsiCo’s technology development spans product innovation, digital transformation, and sustainability—supported by critical key resources like proprietary R&D, global talent, and scalable tech platforms.. It operates global R&D centers to enhance flavors, nutrition, and packaging. Digital initiatives include AI-powered demand forecasting and smart vending machines that personalize product offerings.
Sustainability innovations, like biodegradable packaging and water-efficient technologies, align with its “pep+” (PepsiCo Positive) agenda. The company also invests in e-commerce infrastructure and consumer data analytics to improve digital engagement.
These technological advancements increase efficiency, meet evolving consumer preferences, and drive long-term growth through continuous innovation.
Procurement
PepsiCo’s procurement strategy focuses on cost-effective sourcing while ensuring quality and sustainability. The company builds long-term relationships with trusted suppliers and leverages its scale to negotiate favorable terms. Procurement teams assess supplier performance on ethics, safety, and environmental metrics.
Digital tools support real-time procurement analytics and supplier risk management. PepsiCo also sources locally where possible to reduce carbon footprint and support regional economies.
By combining strategic sourcing with responsible practices, procurement enhances PepsiCo’s supply chain resilience and operational efficiency.
Analysis of PepsiCo’s Competitive Advantage
PepsiCo’s competitive edge arises from the seamless integration of its primary and support activities, allowing it to operate efficiently, innovate consistently, and adapt globally. Its expansive, agile supply chain ensures timely product availability to diverse customer segments, while sustainability practices across sourcing, operations, and logistics reduce costs and meet stakeholder expectations.
Innovation is another cornerstone. Through R&D and digital transformation, PepsiCo launches health-forward products and improves customer experience across platforms. Its ability to leverage consumer insights and adapt its offerings quickly strengthens market responsiveness.
Brand equity also plays a major role. PepsiCo’s diverse portfolio appeals to multiple demographics, supported by culturally relevant marketing that deepens loyalty. Meanwhile, support functions like talent development and advanced procurement strategies enhance internal capabilities and reduce operational risks.
Together, these interconnected value chain elements enable PepsiCo to outperform competitors in cost management, market reach, and customer retention. This strategic alignment ensures long-term sustainability and growth, even in shifting global markets.
Key Takeaways from PepsiCo Value Chain
PepsiCo’s value chain showcases how strategic alignment of operations, innovation, and sustainability drives competitive advantage. Its primary activities—such as efficient logistics, tech-enhanced operations, and dynamic marketing—ensure product quality, speed to market, and strong consumer appeal.
Support activities like inclusive HR practices, R&D, and responsible sourcing enhance these outcomes, making PepsiCo resilient and adaptive. By integrating digital tools, global insights, and sustainability goals, PepsiCo sustains both profitability and brand trust. The value chain framework highlights how every function—individually and collectively—contributes to long-term success and global leadership.
 Insurtech Business Models
Insurtech Business Models  Business Model Metrics and KPIs
Business Model Metrics and KPIs  The Perfect Business Plan
The Perfect Business Plan  Cost Models
Cost Models  Web 3.0 Business Models
Web 3.0 Business Models  Super Guides Bundle
Super Guides Bundle  LinkedIn Strategies
LinkedIn Strategies  Pricing Strategies for Digital Products
Pricing Strategies for Digital Products  Digital Marketing Agency Management
Digital Marketing Agency Management  Company Vision Statements
Company Vision Statements  Marketing Automation
Marketing Automation  Lead Generation
Lead Generation  Sales Enablement
Sales Enablement  Pricing Strategies for Retailers
Pricing Strategies for Retailers  Customer Journey
Customer Journey  Cognitive Biases
Cognitive Biases  OKR Essentials
OKR Essentials  Pricing Strategies for Service Providers
Pricing Strategies for Service Providers  10 Most Profitable Business Models in 2023
10 Most Profitable Business Models in 2023  Project Management Frameworks
Project Management Frameworks  Startup Funding Strategies
Startup Funding Strategies  Top 100 Venture Capital Firms
Top 100 Venture Capital Firms  Negotiation Strategies and Techniques
Negotiation Strategies and Techniques  Hotel Business Models
Hotel Business Models  Pricing Strategies for SaaS
Pricing Strategies for SaaS  Growth Hacking Techniques
Growth Hacking Techniques  Business Model Evolution
Business Model Evolution  Business Model Assessment
Business Model Assessment  Consulting Business Models
Consulting Business Models  Fintech Business Models
Fintech Business Models  170+ Business Model Canvas Examples
170+ Business Model Canvas Examples  Business Model Innovation with ChatGPT
Business Model Innovation with ChatGPT  10 Innovative Business Models for Childcare and Early Education
10 Innovative Business Models for Childcare and Early Education  10 Innovative Business Models for Waste Management and Recycling
10 Innovative Business Models for Waste Management and Recycling  10 Innovative Business Models for Personal Finance and Wealth Management
10 Innovative Business Models for Personal Finance and Wealth Management  10 Innovative Business Models for Subscription Products & Services
10 Innovative Business Models for Subscription Products & Services  10 Innovative Business Models for Space Technology and Services
10 Innovative Business Models for Space Technology and Services  10 Innovative Business Models for Educational Tech Startups
10 Innovative Business Models for Educational Tech Startups  10 Innovative Business Models for Urban Farming
10 Innovative Business Models for Urban Farming  10 Innovative Business Models for Flower Shops
10 Innovative Business Models for Flower Shops  10 Innovative Business Models for Coffee Shops
10 Innovative Business Models for Coffee Shops  10 Innovative Business Models for Jewelry Stores
10 Innovative Business Models for Jewelry Stores  10 Innovative Business Models for 3D Printing Services
10 Innovative Business Models for 3D Printing Services  10 Innovative Business Models for Sustainable Fashion
10 Innovative Business Models for Sustainable Fashion  10 Innovative Business Models for Yoga Studios
10 Innovative Business Models for Yoga Studios  10 Innovative Business Models for Plant-Based Foods and Alternatives
10 Innovative Business Models for Plant-Based Foods and Alternatives  10 Innovative Business Models for Bookstores
10 Innovative Business Models for Bookstores  10 Innovative Business Models for Mobile App Development
10 Innovative Business Models for Mobile App Development  10 Innovative Business Models for Elder Care Services
10 Innovative Business Models for Elder Care Services  10 Innovative Business Models for Biotechnology
10 Innovative Business Models for Biotechnology  10 Innovative Business Models for Renewable Energy Solutions
10 Innovative Business Models for Renewable Energy Solutions  10 Innovative Business Models for Smart Home Technology
10 Innovative Business Models for Smart Home Technology  10 Innovative Business Models for eSports and Gaming
10 Innovative Business Models for eSports and Gaming  10 Innovative Business Models for Drone Technology and Services
10 Innovative Business Models for Drone Technology and Services  Business Model Canvas SWOT Analysis Assesment Excel Spreadsheet
Business Model Canvas SWOT Analysis Assesment Excel Spreadsheet