Tesco Value Chain Analysis
Tesco value chain analysis provides insights into how the UK’s largest retailer delivers exceptional value through strategic coordination of its operations. Originally conceptualized by Michael Porter, value chain analysis distinguishes between primary activities—those directly involved in product creation and delivery—and support activities that bolster these core functions.
For Tesco, this framework illuminates how its extensive network of stores, global sourcing strategies, and customer-centric innovations contribute to both operational efficiency and profitability. By dissecting Tesco’s value chain, we can better understand how the company maintains a competitive edge in the fast-evolving retail sector.
This analysis highlights the systematic efforts Tesco employs to streamline supply chains, embrace digital transformation, and prioritize customer loyalty—all while managing cost structures effectively. Ultimately, understanding Tesco’s value chain reveals how the company sustains market leadership and adapts to modern retail challenges.
Contents
Overview of Tesco
Founded in 1919 by Jack Cohen, Tesco began as a market stall in London and has grown into one of the world’s largest retailers. The Tesco business model evolved rapidly through the 20th century, expanding from groceries into banking, mobile services, and more. A major milestone was the launch of its Clubcard loyalty program in 1995, revolutionizing customer data usage in retail.
The early 2000s saw international expansion across Europe and Asia, along with ventures into convenience and online formats. In recent years, Tesco has streamlined operations, exiting unprofitable markets and reinforcing its core UK operations.
Acquisitions like Booker Group in 2018 diversified its wholesale and foodservice reach, echoing vertical integration moves seen in Costco’s value chain. With a strong emphasis on value, quality, and digital transformation, the Tesco business model continues to adapt to consumer expectations while leading in omnichannel retail.
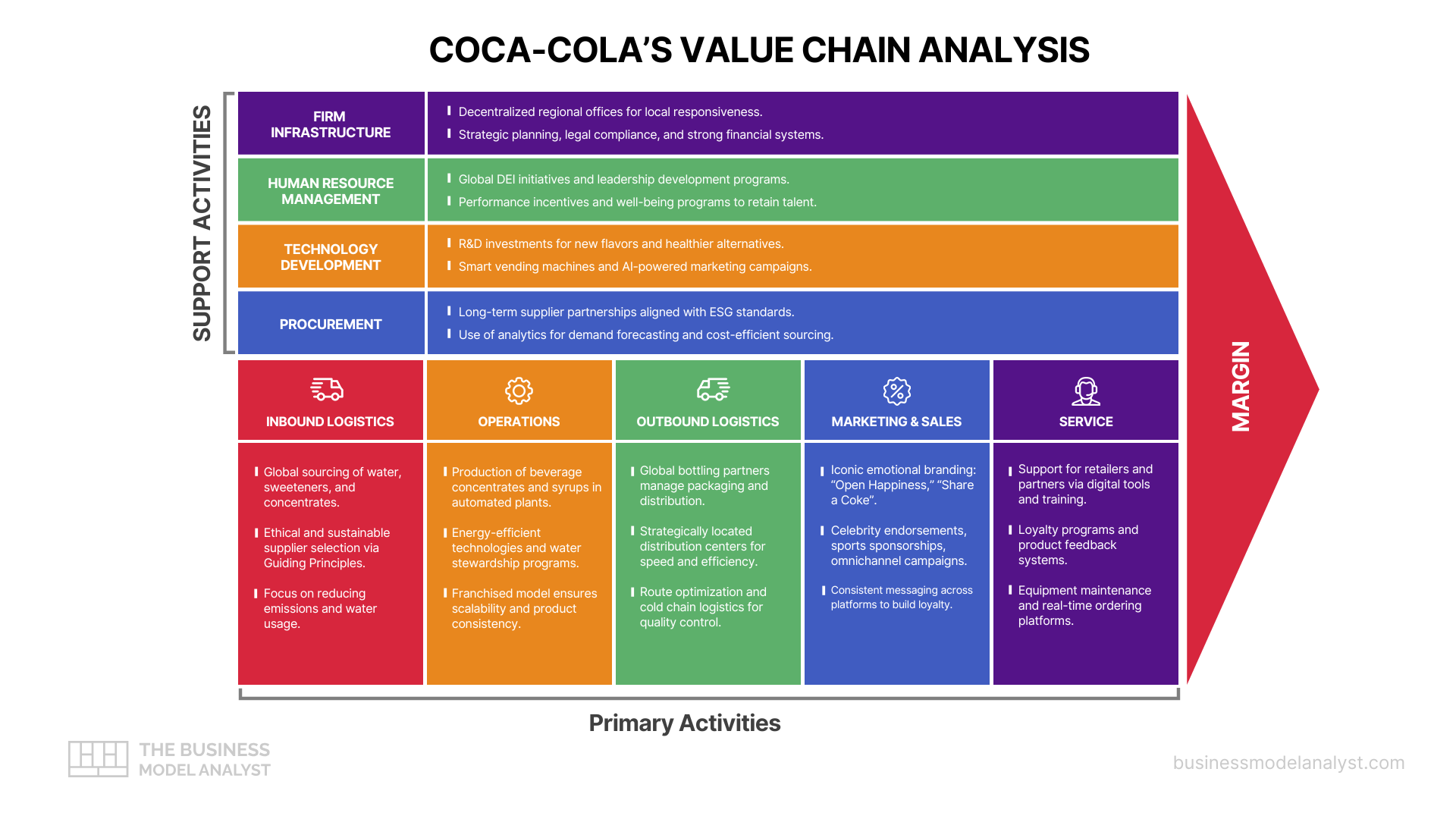
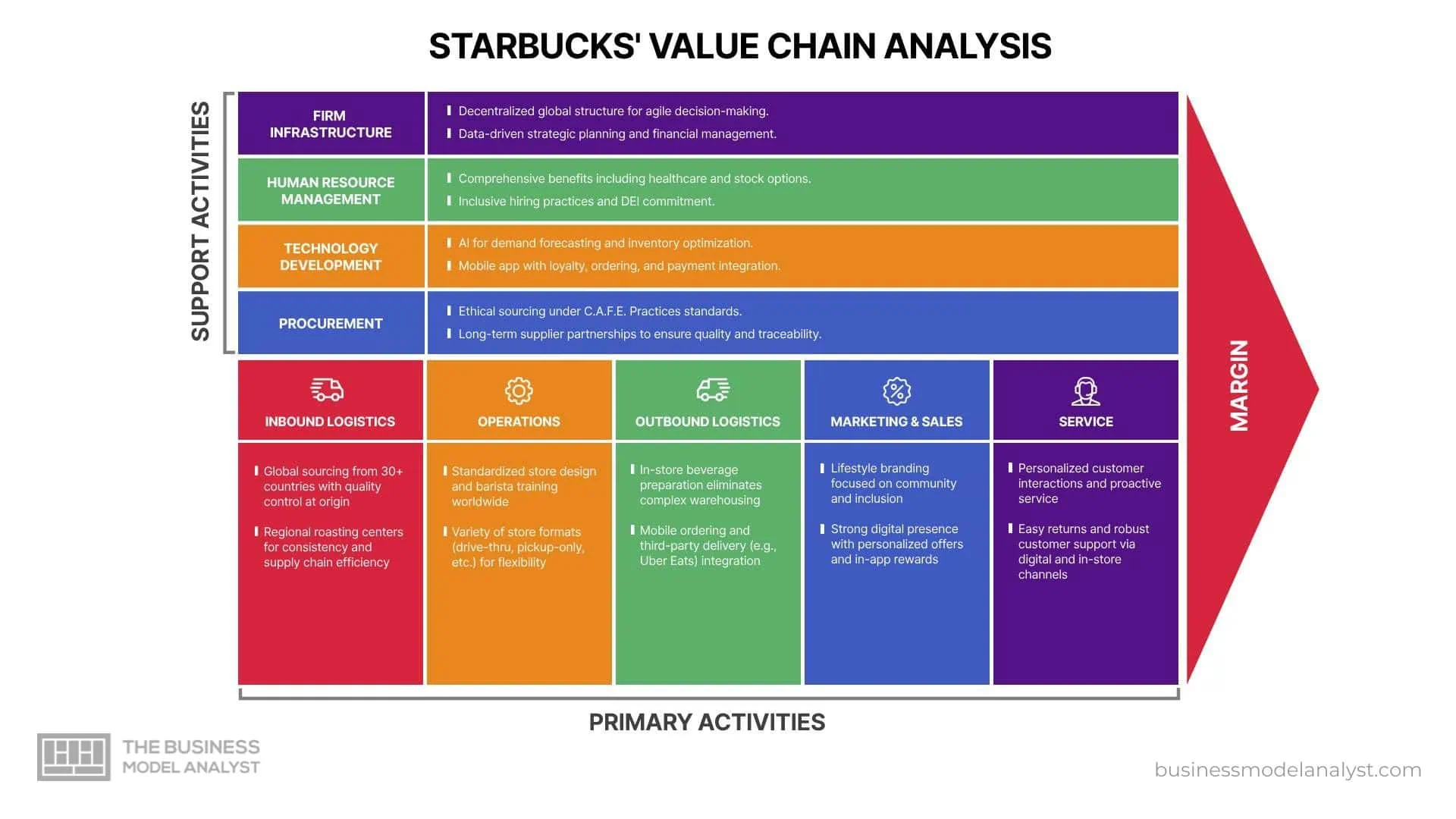
Primary Activities in Tesco Value Chain
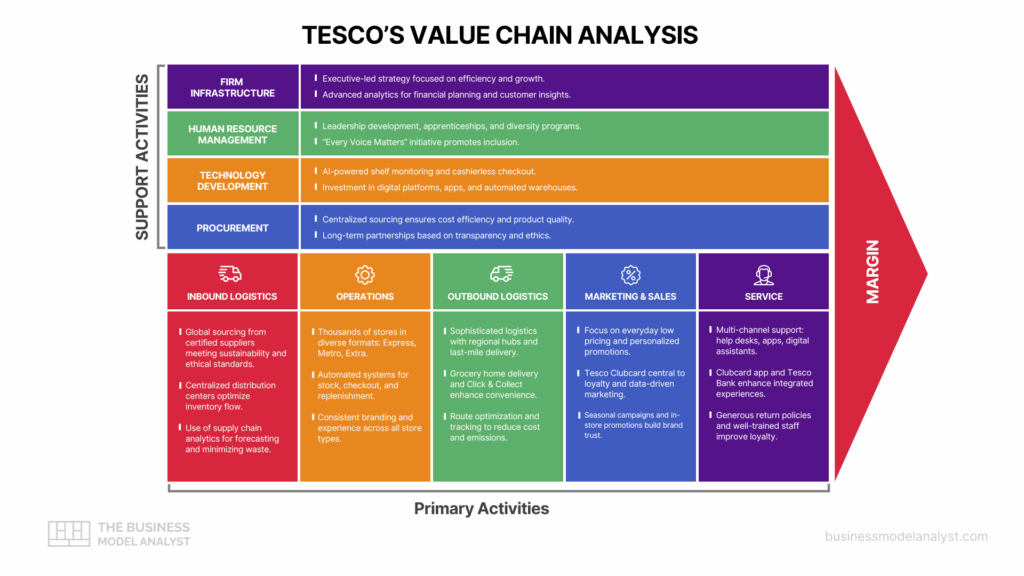
Inbound Logistics
Tesco’s inbound logistics involve sourcing products from a global supplier network—an area that overlaps with sustainable sourcing strategies detailed in the Sainsbury’s SWOT analysis, another major UK retailer. The company prioritizes relationships with certified suppliers that meet its sustainability, quality, and ethical standards. With centralized distribution centers, Tesco ensures inventory flows smoothly from source to store. Initiatives like the Tesco Sustainable Farming Group exemplify its commitment to traceability and environmental responsibility. Advanced supply chain analytics enhance demand forecasting, minimizing waste and ensuring on-shelf availability.
Operations
Tesco operates thousands of stores worldwide in various formats—Express, Metro, Superstore, and Extra. Each format serves a different customer need, with consistent branding and service. Tesco has also invested in automated systems for stock control, checkout efficiency, and shelf replenishment. Self-service kiosks and scan-as-you-shop tools improve the in-store experience. These operational enhancements boost productivity, reduce labor costs, and maintain a uniform customer experience across its retail footprint.
Outbound Logistics
Tesco’s outbound logistics cover the distribution of products to its stores and directly to customers through online channels. The company runs a sophisticated logistics network, including regional distribution centers and last-mile delivery services. Its grocery home delivery and Click & Collect options are pivotal to its omnichannel strategy. Tesco leverages route optimization and real-time tracking to reduce costs and environmental impact while maintaining timely deliveries.
Marketing and Sales
Tesco’s marketing strategy emphasizes everyday low prices, personalized promotions, and strong community ties. Its Clubcard loyalty program is central, collecting data to tailor offers and communications. Advertising spans TV, online, and in-store promotions. Seasonal campaigns and product placement reinforce Tesco’s image as a value-oriented and customer-friendly retailer. These efforts build trust, encourage repeat purchases, and differentiate Tesco in a highly competitive market.
Service
Tesco ensures high-quality customer service through various touchpoints—help desks, mobile apps, and digital assistants—mirroring omnichannel strategies outlined in the Walmart value chain. The Clubcard app and Tesco Bank offer integrated service experiences. Generous return policies and accessible customer support enhance satisfaction. Tesco’s investment in training staff ensures knowledgeable and courteous service, reinforcing loyalty. This comprehensive service approach strengthens customer relationships and enhances the overall brand experience.
Support Activities in Tesco Value Chain
Firm Infrastructure
Tesco’s firm infrastructure encompasses leadership, governance, and performance management systems. The company is led by an executive team focused on long-term strategy and operational efficiency. It employs advanced analytics for financial planning and customer insights, aligning resources with performance goals. Compliance with regulatory frameworks and cost control initiatives ensure Tesco operates ethically and efficiently in multiple markets.
Human Resource Management
Tesco places strong emphasis on attracting and developing talent across its retail and corporate operations. Its HR strategy includes leadership development, apprenticeship schemes, and diversity programs. Tesco’s “Every Voice Matters” initiative promotes inclusion, while competitive wages and training pathways boost engagement. By nurturing employee growth and satisfaction, Tesco enhances productivity and reduces turnover, supporting a resilient and motivated workforce.
Technology Development
Tesco integrates cutting-edge technology across its operations to drive innovation, from automation to AI tools—an approach also adopted by Amazon in its value chain. From AI-powered shelf monitoring to cashierless checkout trials, technology enhances both efficiency and customer experience. The company invests in digital platforms like the Tesco app and automated warehouses. These initiatives support supply chain accuracy, reduce costs, and provide seamless shopping journeys, reinforcing Tesco’s adaptability in an evolving digital retail landscape.
Procurement
Tesco’s procurement processes focus on sourcing high-quality products at scale. It maintains long-term supplier relationships based on transparency and ethical practices. Centralized procurement ensures consistency and cost efficiency, while product quality is safeguarded through rigorous standards. Tesco’s joint ventures and sourcing alliances further enhance its buying power, allowing competitive pricing and improved supplier collaboration.
Analysis of Tesco’s Competitive Advantage
Tesco’s value chain reveals a deeply integrated system where each activity contributes to its dominant position in UK retail. Its strategic procurement and centralized distribution centers reduce costs and ensure product availability. Tesco’s omnichannel model—combining physical stores with robust online platforms—offers unmatched convenience.
The Clubcard program enhances customer loyalty through personalized rewards, reinforcing brand preference. Technology-driven efficiencies, from supply chain management to digital customer engagement, differentiate Tesco in a price-sensitive market. Moreover, the company’s investments in staff training, ethical sourcing, and sustainability demonstrate long-term strategic vision.
By harmonizing operational efficiency with customer-centric innovation, Tesco builds a resilient competitive edge that is difficult for rivals to replicate. These interconnected activities not only support Tesco’s market leadership but also provide the adaptability required to navigate future retail challenges.
Key Takeaways from Tesco Value Chain
Tesco’s value chain demonstrates how strategic coordination across all business activities fosters sustained competitive advantage. Its efficient inbound logistics and technology-driven operations reduce costs while ensuring product availability. Outbound logistics and digital platforms enhance customer access and satisfaction. Support functions, including a strong HR strategy and innovative procurement, reinforce core retail capabilities. By aligning operational excellence with customer loyalty initiatives like Clubcard, Tesco not only improves profitability but also deepens its market presence. This integrated approach enables Tesco to respond swiftly to industry changes while upholding its value-driven promise.