WeWork Value Chain Analysis
WeWork value chain analysis provides insight into how the flexible workspace provider creates, delivers, and sustains value. Originating from Michael Porter’s framework, the value chain dissects a company’s activities into primary and support functions, helping to identify sources of competitive advantage.
For WeWork, a company that revolutionized office space by offering shared, on-demand work environments, its value chain is pivotal in achieving profitability and operational efficiency. Through strategic real estate partnerships, design innovations, and technology-driven services, WeWork streamlines how businesses and freelancers access premium workspace. By analyzing these interconnected activities—from logistics to customer service—we gain clarity on how WeWork sustains its brand presence and adapts to evolving work models.
This analysis highlights the deliberate integration of core processes and support systems that allow WeWork to optimize costs, elevate user experience, and stay agile in a competitive and shifting commercial real estate landscape.
Contents
Overview of WeWork
Founded in 2010 by Adam Neumann and Miguel McKelvey, WeWork began as a disruptive force in commercial real estate. Headquartered in New York City, the company offered flexible, shared workspaces tailored for freelancers, startups, and enterprises. Its early success was driven by urban expansion, millennial work trends, and a strong community-based ethos.
WeWork’s business model revolves around long-term leases with property owners, which are redesigned and subleased to clients on flexible terms. This asset-light approach scaled rapidly across global cities, leading to a peak valuation near $47 billion in 2019. However, after a failed IPO and leadership restructuring, WeWork pivoted toward a more sustainable model focused on cost control and enterprise services.
Key milestones include the acquisition of companies like Meetup and Managed by Q, and a major rebranding under new leadership that positioned WeWork as a service-first platform. Today, the WeWork business model blends physical space with technology-driven workplace solutions, supporting hybrid work and corporate agility worldwide.
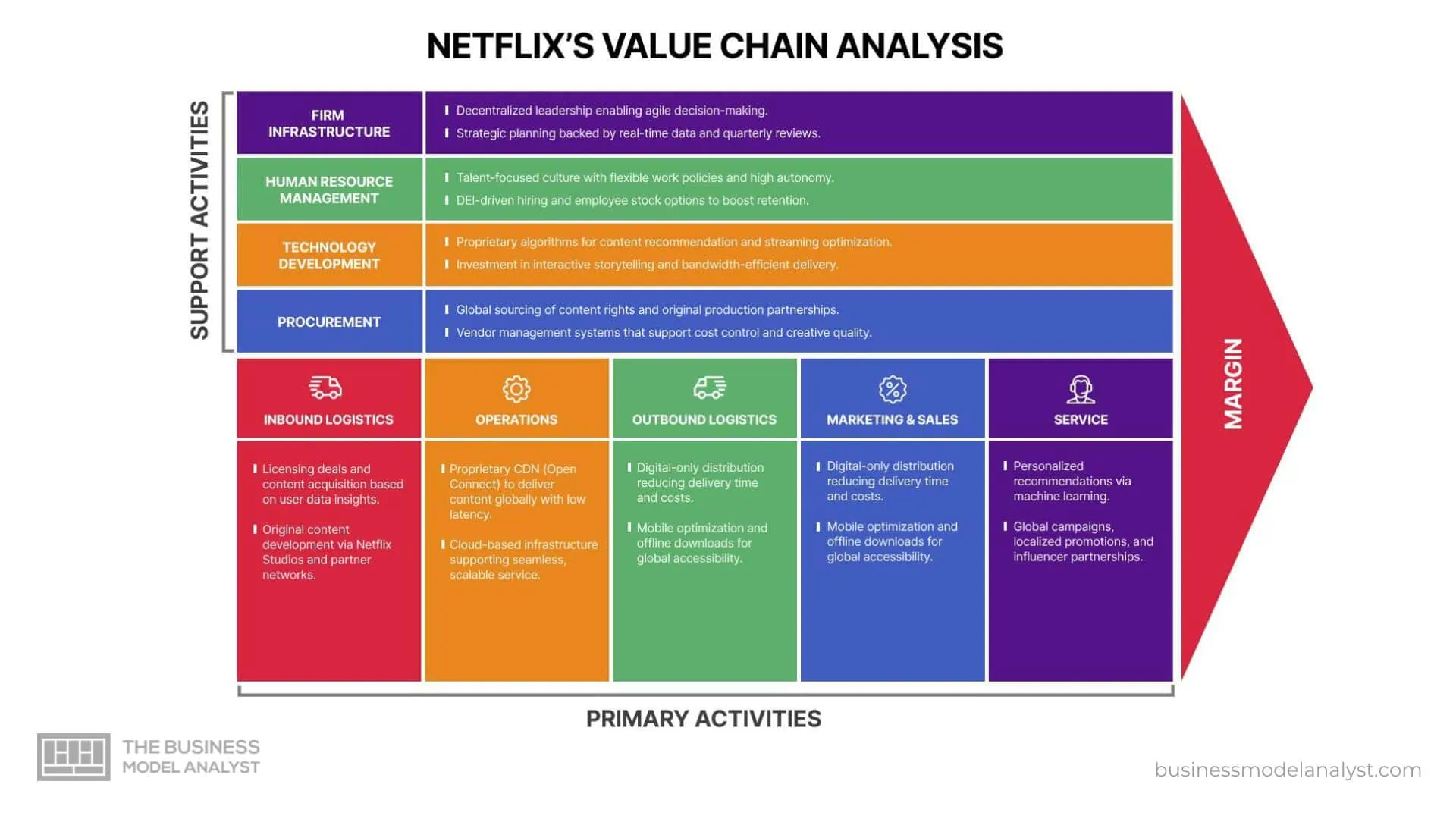
Primary Activities in WeWork Value Chain

Inbound Logistics
WeWork’s inbound logistics center on real estate acquisition, lease negotiation, and vendor coordination. The company secures long-term leases in prime urban locations, transforming them into modern workspaces. Strategic sourcing involves collaborating with real estate developers and landlords—positioning WeWork as a multisided platform that connects space owners with modern tenants through shared value.
Environmental sustainability is prioritized during build-outs, incorporating eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient systems. WeWork’s global procurement team manages furniture, design elements, and IT infrastructure to ensure each location meets brand standards. Efficient vendor management and central oversight streamline supply logistics, reduce waste, and support cost-effective expansion across regions.
Operations
WeWork’s operations revolve around designing, maintaining, and managing flexible workspaces tailored to client needs. Each location is customized with ergonomic furniture, ambient lighting, and advanced tech—fostering productivity and collaboration. Operations teams ensure that daily functions, from internet access to facility cleanliness, meet consistent service levels.
Lean principles and data-driven management improve space utilization and operational efficiency. WeWork leverages proprietary software to monitor occupancy trends, optimize layout configurations, and manage member feedback. This enables rapid response to tenant needs while minimizing downtime and resource waste, aligning operations with high service standards.
Outbound Logistics
WeWork’s outbound logistics focus on delivering workspace solutions to clients efficiently. While it doesn’t ship physical goods, it manages access to office space through a seamless booking system. Members can reserve desks or meeting rooms in real time via the WeWork app, streamlining space distribution and availability.
The company operates a decentralized logistics model, with regional teams managing local building access, maintenance, and customer onboarding. Technology ensures smooth check-ins, room scheduling, and service requests. This model reduces overhead and enhances user convenience, making workspace delivery scalable and responsive to fluctuating demand.
Marketing and Sales
WeWork’s marketing strategy blends digital presence with experiential branding. It uses targeted ads, SEO, and social media campaigns to attract freelancers, startups, and enterprise clients. Messaging emphasizes flexibility, community, and the modern hybrid work experience. Strategic use of thought leadership and webinars strengthens brand credibility.
Sales efforts are supported by data analytics, enabling personalized outreach based on business size, industry, or location. WeWork’s enterprise sales team tailors workspace solutions for large clients, often bundling locations and services. Promotions, referral programs, and free trial offers foster user growth and retention—much like a freemium business model, where entry is easy but upsells and features drive monetization.
Service
WeWork delivers member support through on-site community teams, digital help centers, and mobile app functionalities. Staff members handle onboarding, technical issues, and event coordination to foster a collaborative environment. Services such as IT assistance, mail handling, and wellness events elevate the overall experience.
Customer satisfaction is reinforced through quick issue resolution, flexible lease terms, and consistent communication. Members can access 24/7 support via chat or phone, while enterprise clients receive dedicated account management. This personalized service model helps retain clients, reduce churn, and differentiate WeWork in a competitive market.
Support Activities in WeWork Value Chain
Firm Infrastructure
WeWork’s firm infrastructure encompasses leadership, legal, finance, and compliance functions. Following its 2019 restructuring, the company adopted a more disciplined approach to governance and cost management. Leadership emphasizes data-driven decision-making, accountability, and sustainable growth strategies.
Centralized financial systems allow real-time performance tracking across locations. Compliance teams ensure legal adherence, safety regulations, and lease obligations are consistently met worldwide. This solid infrastructure supports operational agility and enables WeWork to scale effectively while minimizing risk exposure and maintaining investor confidence.
Human Resource Management
WeWork’s HR strategy focuses on attracting diverse talent, fostering inclusion, and promoting internal growth. Recruitment prioritizes individuals with customer service, hospitality, and tech backgrounds to align with the company’s service-first ethos. Internal training programs enhance employee engagement and skill development.
The company emphasizes Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives, with dedicated teams working to ensure equitable workplace culture. Employee performance is incentivized through recognition programs and clear advancement pathways. These HR practices improve retention, promote innovation, and ensure a motivated workforce aligned with WeWork’s mission.
Technology Development
WeWork invests heavily in proprietary technology to enhance workspace functionality and member experience. Its digital platforms support desk bookings, event scheduling, access control, and real-time feedback. These tools improve operational oversight and allow seamless user interaction with physical spaces.
Data analytics help optimize space usage and guide expansion strategies. The company also explores IoT and AI solutions—an innovation mindset deeply aligned with Lean Canvas principles, where iterative testing and feedback drive continuous value creation. These innovations strengthen customer satisfaction, reduce energy waste, and reinforce WeWork’s position as a tech-forward workspace provider.
Procurement
WeWork’s procurement strategy focuses on sourcing high-quality furnishings, building materials, and technology systems at competitive costs. The centralized procurement team negotiates bulk deals with global vendors, ensuring consistency and cost efficiency across locations.
The company prioritizes suppliers who share its sustainability values—favoring eco-certified materials and energy-efficient equipment. Through standardized purchasing and strong vendor relationships, WeWork maintains brand coherence, minimizes project delays, and ensures operational readiness at each new site. Effective procurement directly supports cost control and workspace quality.
Analysis of WeWork’s Competitive Advantage
WeWork’s value chain reveals a competitive edge rooted in flexible space delivery, strong service culture, and integrated technology. By controlling design and operations across a global network, WeWork ensures consistency and adaptability—key traits for businesses navigating hybrid work models.
Its streamlined primary activities—from real estate procurement to member support—enable faster market entry and scalable service. Meanwhile, robust support functions, like centralized procurement and tech innovation, reduce overhead and enhance user experience. This synergy fosters cost efficiency and brand reliability.
Compared to traditional office providers, WeWork stands out through its digital-first, customer-centric model. Customizable plans, responsive support, and global access give clients unmatched agility. Additionally, its evolving workplace solutions help enterprises de-risk real estate commitments and respond to employee flexibility needs.
Long-term sustainability lies in WeWork’s ability to blend hospitality with technology while maintaining fiscal discipline. This positions the company to adapt to future shifts in how and where people work—strengthening its value proposition in a dynamic market.
Key Takeaways from WeWork Value Chain
WeWork leverages a tightly integrated value chain to deliver flexible, tech-enabled workspaces that meet evolving business needs. Its primary activities—spanning strategic site sourcing, agile operations, and responsive customer service—allow for high scalability and user satisfaction.
Support functions such as centralized procurement, innovative technology development, and inclusive talent strategies reinforce operational excellence. Together, these activities reduce costs, enhance agility, and build brand loyalty.
By aligning its value chain with shifting workplace dynamics, WeWork positions itself as a resilient, forward-looking leader in the flexible workspace market.